The multimedia specification allows the merging of uncompressed full HD digital video, audio, Ethernet, power and control.
By Daniel Feldman, Microsemi
HDBase-T technology is emerging as an important digital connectivity standard that will enable five key elements to share the same low-cost Category 5e or Category 6 network cabling infrastructure: 1) uncompressed full HD video, 2) uncompressed full HD audio, 3) 100Base-T Ethernet, 4) control signals, and 5) power. HDBase-T's ability to deliver up to 100 watts (W) of power to network devices is a first for transport technology. It gives users significantly more flexibility for installing wall-hung TVs and other products throughout the home, while providing new opportunities to manage and significantly reduce overall network power consumption.
The power behind these new capabilities is Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology, which has revolutionized enterprise and network deployment by enabling devices like wireless access points, video surveillance cameras and access control systems to be installed wherever they are needed, including difficult-to-reach locations, regardless of whether or not there is an electrical outlet nearby. PoE technology will be incorporated into the HDBase-T standard to enable power delivery to a wide range of consumer electronic products including TVs of virtually any size. It is no longer necessary for the powered device's (PD's) electrical jack to be connected to a power supply. All PDs can now be deployed in the ideal location regardless of electrical outlet availability. They can be monitored and reset over the network as desired, and they can operate during a power failure using centralized power sourcing equipment (PSE) backup power.
HDBase-T advantages
HDBase-T technology connects home entertainment systems and devices using a trademarked feature called 5Play that enables up to 10.2 Gbits/sec of uncompressed video and audio, 100Base-T Ethernet, control signals and power to share the same cable, across distances up to 100 meters using standard RJ45 (8-pin, 8-conductor) connectors.
HDBase-T technology is designed to scale up to 20 Gbits/sec of multi-stream video and audio throughput, and can also support up to eight, 100-meter cable hops. HDBase-T also has the capacity to support double the resolution of today's video content, which will be required for 3D integration and future 2k and 4k formats. Unlike other technologies that require a specific cable and/or a new, proprietary connector, HDBase-T uses existing Category 5e/6 infrastructure.
The HDBase-T Alliance's whole-home connectivity concept is based on the trademarked feature called 5Play, which operates over up to 100 meters of Category 5e or Category 6 cabling.
HDBase-T's powering capabilities are increasingly important as consumers bring more and more electronic devices into the home. Using HDBase-T, a single LAN cable can provide up to 100 W of power, over distances up to 100 meters, requiring no additional power source. The technology has enough headroom to power the vast majority of these products. For example, today's typical 40-inch LED TV requires 70 W of power, and beginning this month (September 2011), the latest Energy Star 5.3 specifications restrict all TVs to 108 W of power consumption, regardless of screen size. Energy Star 6.0 is targeting a cap of 85 W for all screen sizes from mid-2012. LCD and LED TV monitors are rapidly approaching an average of approximately one W per inch of screen size. At these levels, HDBase-T has ample power-delivery capabilities, even for supporting very large displays.
HDBase-T power capabilities also solve the problem manufacturers have faced with providing thinner, lighter wall-mounted TVs that have been encumbered by complicated companion AC-to-DC and DC-to-DC power circuitry. HDBase-T replaces this AC-to-DC circuitry with a single, convenient cable/connector so that, for instance, wall-hung TVs connected via an HDBase-T-enabled Category 5e/6 cable will require no other power source.
Additionally, HDBase-T's power-delivery technology provides the foundation for new opportunities to manage overall power consumption and efficiency. These capabilities are enabled by the underlying PoE technology that has become a critical element of the latest power-over-HDBase-T (PoH) specifications.
More PoE power, better efficiency
The original, low-power IEEE 802.3af standard used two of the four pairs of wires in a Category 5e cable, while the more recent IEEE 802.3at-2009, or "PoE Plus" specification enables power to be delivered over all four pairs. These latest PoE specifications also add mechanisms for device detection, classification, disconnection, and protection from overload/short conditions, while also adding new "smart" energy-management capabilities.
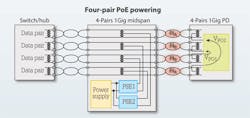
In a typical PoH implementation, the power sourcing equipment (PSE) is installed and powered by a 50- to 57-volt DC power supply, and all PDs then receive power directly over the HDBase-T link across all four pairs of Category-5-or-better cables. Four-pair powering is the key to delivering more power with greater efficiency. Defined in the latest high-power PoE standards, four-pair powering gives PDs two power interfaces so they can receive twice the power of earlier two-pair solutions. Nothing precludes the two power interfaces from being connected–one over the two pairs using lines 1, 2, 3 and 6 and the other using the two pairs that use lines 4, 5, 7 and 8. This is what makes it possible to increase power delivery while fully complying with the standard.
Four-pair powering is defined in the latest high-power Power over Ethernet standard. It gives powered devices two power interfaces. Nothing precludes the two interfaces from being connected.
Additionally, core PoE technology has been enhanced for the PoH specification to include a higher current of almost 1 Amp (A) for every two pairs, with an appropriate three-event classification that identifies PoH PSEs. This enables PoH technology to transfer up to 100 W of continuous DC power, per port, from one side of the HDBase-T link to the other. Unlike in PoE, where the PD must assume a worst-case cabling infrastructure at all times, PoH enables the PD to identify the cable length/resistance and draw more power, as long as the overall power consumption does not exceed 100 W. PoH is fully backward-compatible with the IEEE 802.3at-2009 specification, including the Section 33.7.1 mandate that all PSE conform to IEC 60950-1:2001 and be classified as a Limited Power Source (LPS) carrying no more than 100 volt-ampere (VA) per port without the need for special overcurrent protection devices. PoH also does not infringe on any of the mandated PoE safety requirements.
Corporate America is already well aware of the power savings that are possible using PoE technology. Network administrators use PoE-enabled equipment called midspans that feature remote PD monitoring and configuration capabilities to significantly reduce power consumption, system-wide.
With PoH solutions, adding 100 W per port inside an Ethernet/HDBase-T switch presents a daunting engineering task that can greatly reduce overall system reliability. Midspans become the ideal solution for commercial applications such as display signage, in which a 24-port PoH midspan can be used to power 24 PoH-capable displays.
HDBase-T offers the unprecedented opportunity to merge uncompressed full HD digital video, audio, 100Base-T Ethernet, power and various control signals onto a single 100-meter Category 5e/6 cable equipped with 8P8C connectors and PoH power-delivery technology. PoH is a key element of the HDBase-T standard, and draws upon the same PoH technology that has been proven in enterprise networking and IP-based security and surveillance systems for the past decade. Now this technology is being used to deliver a high-performance, high-quality consumer multimedia experience at very low power-consumption rates.
PoE silicon developments
The latest developments in Power over Ethernet silicon, including the latest PoE Manager integrated circuits from Microsemi, implement four-pair powering while supporting the higher currents required by HDBase-T (including the additional PoH classification requirements), which enables designers to optimize their systems for low power dissipation and a small footprint. These PSE devices also feature a variety of new capabilities including dynamic power management, which cuts system costs as much as 40 percent by enabling the use of smaller power supplies. Today's PSE devices also enable multiple power supplies to be used, added in a granular fashion for emergency power management, and shared between multiple switches using the latest backplane power-management techniques. Finally, today's PoE Manager ICs feature resilient power management, which increases system resilience while maximizing power supply use. Together, these capabilities contribute to power dissipation reductions of 10 percent on the chip and 15 percent on the cable, while enabling a system footprint up to 50 percent smaller than earlier PoE solutions. -D.F.
Daniel Feldman is business unit manager, communications power with Microsemi (www.microsemi.com).
Past CIM Issues